What Does The Enzyme Helicase Do
What Does The Enzyme Helicase Do. Share on pinterest enzyme lock and key model. Which way does helicase move?

 DNA Replication Tutorial (high school level from www.sciencemusicvideos.com
DNA Replication Tutorial (high school level from www.sciencemusicvideos.comThe enzyme rna polymerase binds to the template strand of dna at the beginning of the sequence to be copied. Similarly, it is asked, why does dna replication occur in the 5 to 3 direction? Dna helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the dna double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds down the center of the strand.

The first eukaryotic dna helicase discovered was in 1978 in the lily plant. Helicase's job is to move the replication forks forward by unwinding the dna (breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base pairs).
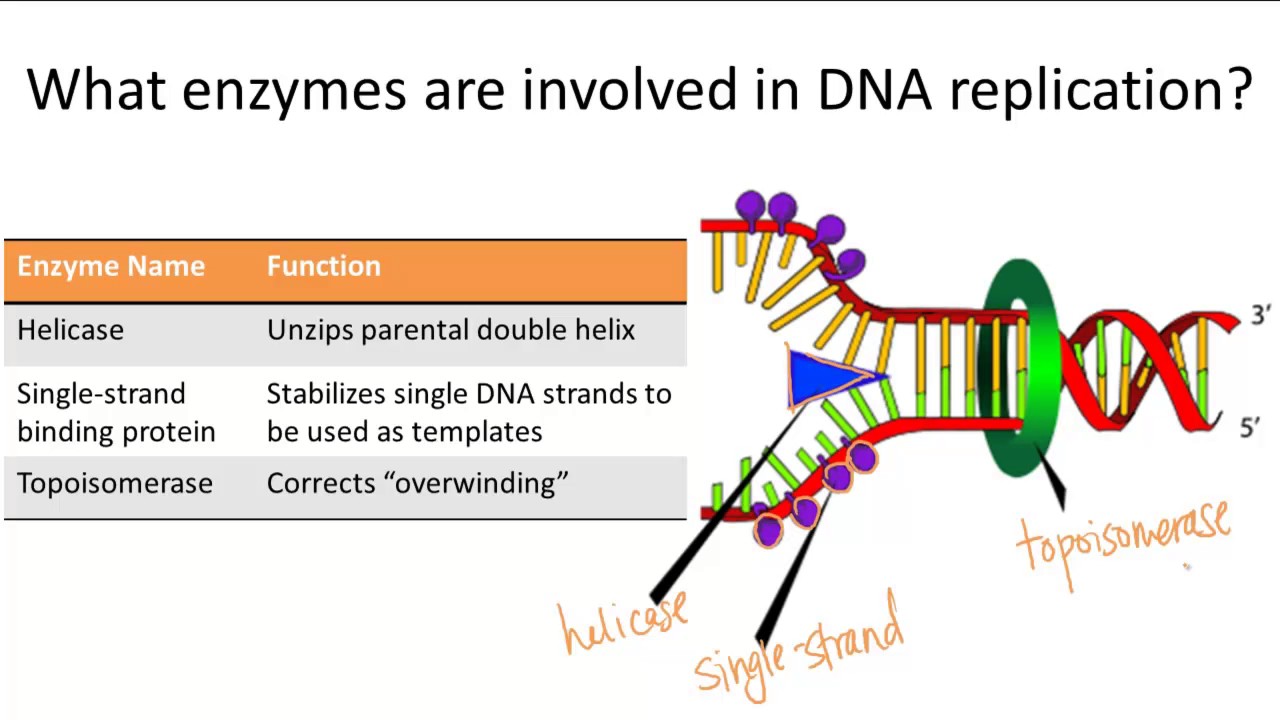
This causes the two strands to separate and unwind, exposing nucleotide bases. Helicase as the name suggests, are enzymes that interacts with nucleic acids such as dna or rna and remodel them by relaxing their helix.
Helicase is the enzyme that breaks down dna by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the two strands. Share on pinterest enzyme lock and key model.
It begins at a site called the origin of replication, and it creates a replication fork by separating the two sides of the parental dna. Share on pinterest enzyme lock and key model.
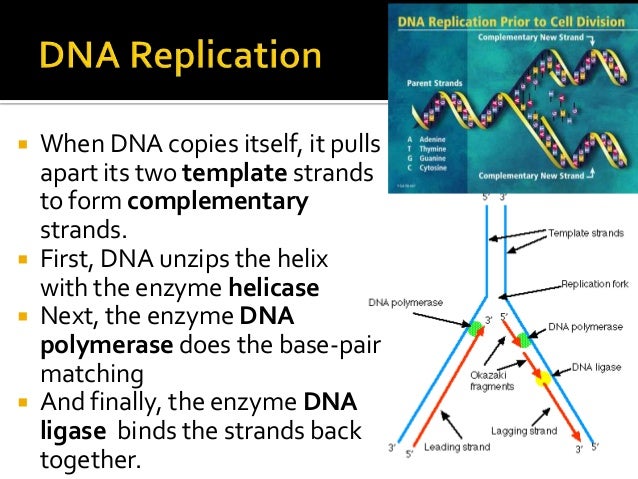
Dna helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the dna double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds down the center of the strand. We are learning dna replication and enzymes involved in dna replication.
A helicase is an enzyme that unzips joined strands of deoxyribonucleic acid or ribonucleic acid. The helicase is a class of the enzyme, especially, the dna helicase that unwinds the dsdna and facilitates dna replication.
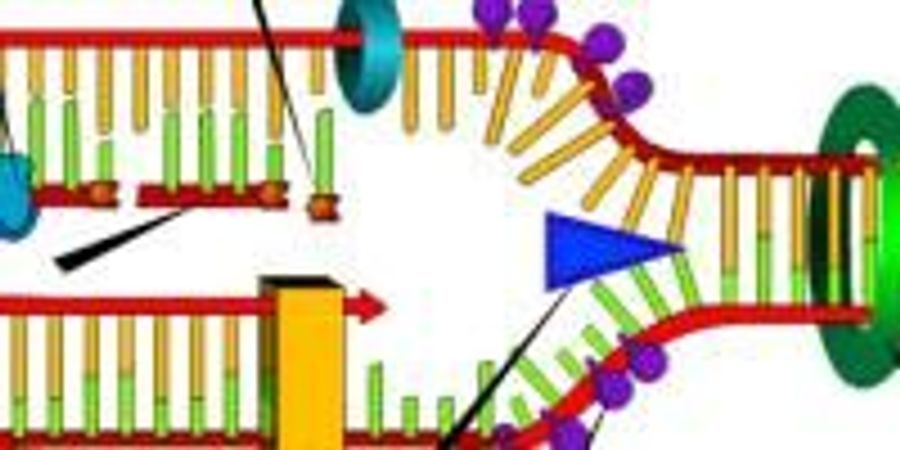
The "lock and key" model was first proposed in 1894. It begins at a site called the origin of replication, and it creates a replication fork by separating the two sides of the parental dna.
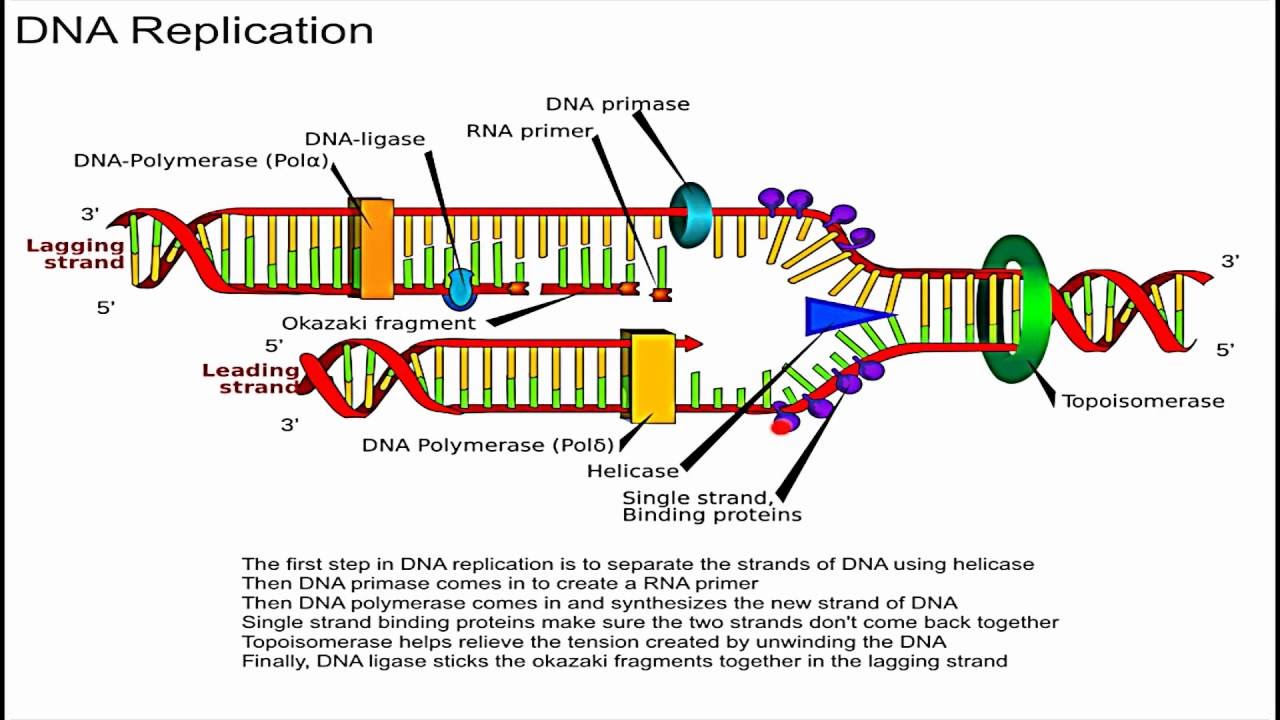
The enzyme dna helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the bases in a specific region of the dna molecule. Helicase is the enzyme that breaks down dna by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the two strands.
Helicases are enzymes that bind and may even remodel nucleic acid or nucleic acid protein complexes. Share on pinterest enzyme lock and key model.
Dna helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the dna double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds down the center of the strand. The "lock and key" model was first proposed in 1894.

The first eukaryotic dna helicase discovered was in 1978 in the lily plant. Dna helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the dna double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds down the center of the strand.

Helicase's job is to move the replication forks forward by unwinding the dna (breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base pairs). Adenine only pairs with thymine and cytosine only binds with guanine.
The helicase is a class of the enzyme, especially, the dna helicase that unwinds the dsdna and facilitates dna replication. Helicases are enzymes that bind and may even remodel nucleic acid or nucleic acid protein complexes.

Dna helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the dna double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds down the center of the strand. To do this, it uses a range of enzymes.
You should now understand that dna helicase has a very important job to do. In order to unwind dna, these interactions between base pairs must be broken.
The helicase is a class of the enzyme, especially, the dna helicase that unwinds the dsdna and facilitates dna replication. It is responsible for opening up our dna to allow for replication as well as transcription of our dna.
Dna helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the dna double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds down the center of the strand. The separation of the two single strands of dna creates a.

Helicase is an enzyme, which are proteins that regulate the cell's biological and chemical reactions. In this model, an enzyme's active.
This causes the two strands to separate and unwind, exposing nucleotide bases. In this model, an enzyme's active.
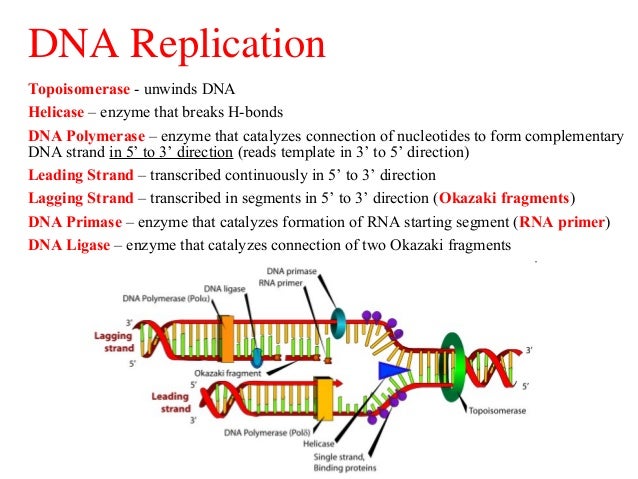
16 what does the enzyme helicase do 17 what does the enzyme dna polymerase do 18 from bio 105 at francis marion university Does the helix work in transcription?
Helicase As The Name Suggests, Are Enzymes That Interacts With Nucleic Acids Such As Dna Or Rna And Remodel Them By Relaxing Their Helix.Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the complementary bases of dna together (a with t, c with g). A helicase is an enzyme that unzips joined strands of deoxyribonucleic acid or ribonucleic acid. The second phase is elongation.
The Dna Polymerase Enzymes Organize, Group, And Establish Order For Nucleotides, These Building Blocks Of Dna And Rna.Helicases are enzymes that bind and may even remodel nucleic acid or nucleic acid protein complexes. In order to unwind dna, these interactions between base pairs must be broken. There are dna and rna helicases.
It Begins At A Site Called The Origin Of Replication, And It Creates A Replication Fork By Separating The Two Sides Of The Parental Dna.The separation of the two single strands of dna creates a. You should now understand that dna helicase has a very important job to do. Helicase is the enzyme that breaks down dna by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the two strands.
Adenine Only Pairs With Thymine And Cytosine Only Binds With Guanine.What does helicase enzyme do? This is performed by an enzyme known as dna helicase. The helicase is a class of the enzyme, especially, the dna helicase that unwinds the dsdna and facilitates dna replication.
The First Eukaryotic Dna Helicase Discovered Was In 1978 In The Lily Plant.Helicase is one of the proteins that regulate dna replication. Other proteins help the helicase to keep the threads apart for as long as it takes for the replication process. Helicase is a group of enzyme that helps unwounds dna by breaking hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases.
Komentar
Posting Komentar